《分布式 Java 应用:基础与实践》第三章总结其一:理解 JVM(未完待续)
0. JVM 大概
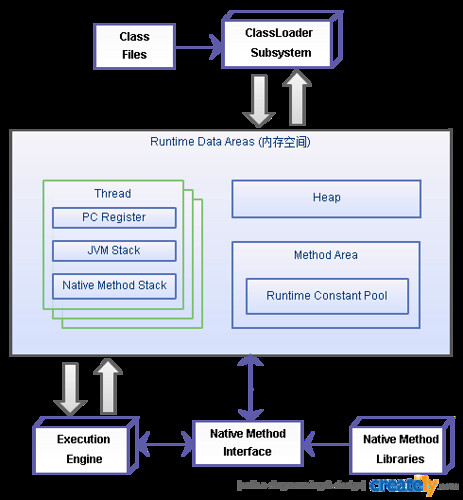
参考了:
- Understanding JVM Internals 的 figure 4
- The Java Virtual Machine –by Bill Venners 的 figure 5-1
1. Java 代码的执行
1.1 编译(javac)
以下还参考了:
The process of compiling a set of source files into a corresponding set of class files is not a simple one, but can be generally divided into three stages. Different parts of source files may proceed through the process at different rates, on an “as needed” basis.
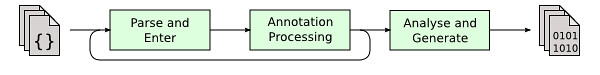
1.1.1 Parse & Enter
Parse 过程包括:
- 词法分析(by
com.sun.tools.javac.parser.Scanner):将代码解析成 Token 序列 - 语法分析(by
com.sun.tools.javac.parser.Parser):根据 Token 序列生成语法树(AST, Abstract Syntax Tree),using aTreeMaker. Syntax trees are built from subtypes ofJCTreewhich implementcom.sun.source.Treeand its subtypes.
Enter 过程接收 AST,将 symbol 输入到 symbol table。The output from this phase is a To Do list, containing trees that need to be analyzed and have class files generated.
鉴于编译原理的知识已经忘得差不多了,这里可以补习一下:
- what is the difference between token and lexeme?
- In compiler construction, is a symbol the same as a token?)
A token is a pair consisting of a token name and an optional attribute value. The token name is an abstract symbol representing a kind of lexical unit, e.g., a particular keyword, or sequence of input characters denoting an identifier. The token names are the input symbols that the parser processes.
A token (name) is not necessarily a symbol in the symbol table. For example, if a token (name) is a reserved word, then it is not entered in the symbol table. If a token (name) is an identifier, then it will likely be entered in the symbol table.
1.1.2 Annotation Processing
If any annotation processors generate any new source or class files, the compilation is restarted, until no new files are created.
比如书上提到的:使用 Lombok 时,private @Getter String username; 会自动帮你生成 getter 方法 public String getUsername() 的代码,此时就要重新进入 Parse & Enter 过程了。
1.1.3 Analyse & Generate
Finally, the syntax trees created by the parser are analyzed and translated into class files. 这里 analyse 是语义分析。
The work to analyse the tree and generate class files is performed by a series of visitors that process the entries on the compiler’s To Do list. There is no requirement that these visitors should be applied in step for all source files, and indeed, memory issues would make that extremely undesireable. The only requirement is that each entry on the To Do list should should eventually be processed by each of these visitors, unless the compilation is terminated early because of errors.
这些 visitor 包括:
- Attr: The top level classes are “attributed”, meaning that names, expressions and other elements within the syntax tree are resolved and associated with the corresponding types and symbols. Many semantic errors may be detected here.
- Flow: If there are no errors so far, flow analysis will be done for the class, including:
- Liveness analysis checks that every statement is reachable.
- Exception analysis ensures that every checked exception that is thrown is declared or caught.
- Definite assignment analysis ensures that each variable is assigned when used.
- Definite unassignment analysis ensures that no final variable is assigned more that once.
- TransTypes: Code involving generic types is translated to code without generic types, using TransTypes.
- Lower: a.k.a. Desugar, which removes syntactic sugar, such as inner classes, class literals, assertions, and foreach loops. For each class that is processed, Lower returns a list of trees for the translated class and all its translated nested and inner classes.
- Gen: 生成 class 文件,具体的步骤包括:
- 将实例成员的 initializer 收集到构造器,将静态成员的 initializer 收集到
<clinit>() - 用 AST 生成字节码,采用的方式是后续遍历 AST,并进行最后的少量代码装换(比如 String + String 变成 StringBuilder)
- 从符号表生成 class 文件
- 将实例成员的 initializer 收集到构造器,将静态成员的 initializer 收集到
留下评论