Moment, Expectation, Variance, Skewness and Kurtosis
0. Dictionary
| English | Chinese | Symbol |
|---|---|---|
| Moment | 矩 | |
| $n^{th}$ | n 阶 | |
| Raw Moment | 原点矩 | $\mu’_n$ |
| Central Moment | 中心矩 | $\mu_n$ |
| Standardized Moment | 标准矩 | $\alpha_n$ |
| Mean | 平均值 | $\mu$ |
| Median | 中位数 | |
| Mode | 众数 | |
| Variance | 方差 | $\sigma^2$ |
| Standard Deviation | 标准差 | $\sigma$ |
| Expectation Operator | 期望算子 | $E[X]$ |
| Skewness [sk’ju:nes] | 偏度 | $\gamma_1$ |
| Kurtosis [kɜ:’təʊsɪs] | 峰度 | $\gamma_2$ |
1. Moment
1.1 Definition in Physics
数学中矩的概念来自于物理学。在物理学中,矩,又称动差,是用来表示物体形状的物理量。
实函数(指定义域和值域均为实数域的函数)$f(x)$ 相对于值 $c$ 的 $n$ 阶矩(the $n^{th}$ moment of a real-valued continuous function $f$ of a real variable x about a value $c$)为:
\[\mu'_n = \int^\infty_{-\infty} (x-c)^n f(x) dx\]1.2 Raw Moment
主要参考 Raw Moment。
In statistics, a raw moment of a univariate continuous random variable $X$ is one of a probability density function (a.k.a pdf) $f(x)$ taken about 0 (i.e. $c = 0$).
\[\mu'_n = \int^\infty_{-\infty} x^n f(x) dx\]Of a discrete random variable $X$:
\[\mu'_n = \sum_{i=1}^k x_i^n P(X = x_i)\]当 n = 1 时,它的意义就是:”$X$ 的取值 $x_i$” 乘以 “$X$ 取 $x_i$ 的概率”,然后求和。
特定地,有 $\mu’_0 = 1$
1.3 Central Moment
主要参考 Central Moment。
A central moment of a univariate continuous random variable $X$ is one of a probability density function $f(x)$ taken about the mean (因为 Expectation (== Mean) 也被称为随机变量的 “中心”,所以 $c = mean(X)$ 的 moment 就被命名为 central moment):
\[\mu_n = \int^\infty_{-\infty} (x-\mu)^n f(x) dx\]特定地,有 $\mu_0 = 1$ 和 $\mu_1 = 0$
1.4 Standardized Moment
\[\alpha_n = \frac{\mu_n}{\sigma^n}\]特定地,有 $\alpha_1 = 0$ 和 $\alpha_2 = 1$
2. Expectation
2.1 Expectation Equals Arithmetic Mean
Expectation is defined as $1^{st}$ raw moment:
\[\mu = \mu'_1 = \int^\infty_{-\infty} x f(x) dx\]Expectation is the arithmetic mean of any random variable coming from any probability distribution,这个不用怀疑,可以参见这篇 Why is expectation the same as the arithmetic mean?。
2.2 Expectation Operator
其实就是把 $\mu$ 看做 a function of $x$:
\[E[X] = \mu = \mu'_1 = \int^\infty_{-\infty} x f(x) dx\]If $Y = g(X)$, then:
\[E[Y] = E[g(X)] = \int^\infty_{-\infty} g(x) f(x) dx\]这个 $E$ 就称为 Expectation Operator。
进而有:
- $E[X^n] = \mu’_n$
- $E[(X-\mu)^n] = \mu_n$
- $E \left [ \big(\frac{X-\mu}{\sigma} \big)^n \right ] = \frac{E[(X-\mu)^n]}{\sigma^n} = \alpha_n$
3. Variance
Variance is defined as $2^{nd}$ central moment:
\[\sigma^2 = \mu_2 = \int^\infty_{-\infty} (x-\mu)^2 f(x) dx = E[(X-\mu)^2] = E[X^2] - \mu^2\]4. Skewness
Skewness is defined as $3^{rd}$ standardized moment:
\[\gamma_1 = \alpha_3 = \frac{\mu_3}{\sigma^3}\]Skewness is a measure of asymmetry [əˈsɪmɪtri]:
- If a distribution is “pulled out” towards higher values (to the right), then it has positive skewness ($\gamma_1 > 0$,称为正偏态或右偏态).
- If it is pulled out toward lower values, then it has negative skewness ($\gamma_1 < 0$,称为负偏态或左偏态).
- A symmetric [sɪ’metrɪk] distribution, e.g., the Gaussian distribution, has zero skewness ($\gamma_1 = 0$).
- 进一步还可以得到:mean == median
- 如果是 symmetric 且是单峰分布,那么还可以得到:mean == median == mode
- 进一步还可以得到:mean == median
注意看图的时候,skewness 是个非常 confusing 的概念:
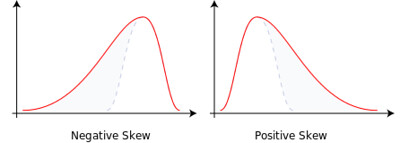
- 左图:Negative skew ($\gamma_1 < 0$) == The distribution is skewed to the LEFT == Mean is on the left side of the peak
- while the peak is pulled towards RIGHT
- 右图:Positive skew ($\gamma_1 > 0$) == The distribution is skewed to the RIGHT == Mean is on the right side of the peak
- while the peak is pulled towards LEFT
所以 skewness 最好不要根据图形去记忆,而应该根据一维坐标轴:D H@ScienceForums.Net:
One way to remember the left/right stuff is that it corresponds with the orientation of the numberline. Since negative numbers are to the left of zero, negative skewness is the same as left-skewed. The same goes for positive skewness and right-skewed.
5. Kurtosis
Kurtosis, from Greek word “kyrtos” for convex, related to word “curve”, is mainly defined by $4^{th}$ standardized moment:
\[\gamma_2 = \alpha_4 - 3 = \frac{\mu_4}{\sigma^4} - 3\]It is also known as excess kurtosis (超值峰度). The “minus 3” at the end of this formula is often explained as a correction to make the kurtosis of the normal distribution equal to zero.
- If $\gamma_2 > 0$,称为尖峰态(leptokurtic, [leptəʊ’kɜ:tɪk])
- If $\gamma_2 < 0$,称为低峰态(platykurtic, [plæ’ti:kɜ:tɪk])。
留下评论