Terminology Recap: Random Variable / Distribution / PMF / PDF / Independence / Marginal Distribution / Joint Distribution / Conditional Random Variable
主要参考:
- NOTES ON PROBABILITY - Greg Lawler
- Measure theory and probability - Alexander Grigoryan
- Lebesgue Measure on $\mathbb{R}^n$ - John K. Hunter
- Conditional random variables - Lawrence Pettit
Prerequisite #1 : $\sigma$-algebra
非常蛋疼的一个事实:$\sigma$-algebra 并不是一个严格意义上的 algebra……
Definition: In mathematical analysis and in probability theory, a $\sigma$-algebra on a set $S$ is a subset $\Sigma \subset 2^S$ that includes $S$ itself. It is closed under complement and countable unions.
- 因为 $S \in \Sigma$ 同时它是 closed under complement,所以 $\varnothing \in \Sigma$
- $\sigma$-algebra, $\sigma$-ring 和 $\sigma$-field 都是有关系的,但这里不表
Prerequisite #2 : Borel Set / Borel $\sigma$-algebra
In mathematics, a Borel set is any set in a topological space that can be formed from open sets (or, equivalently, from closed sets) through the operations of countable union, countable intersection, and relative complement.
- relative complement of $A$ in $B$ 就是 $A - B$
- relative complement of $B$ in $A$ 就是 $B - A$
For a topological space $X$, the collection of all Borel sets on $X$ forms a $\sigma$-algebra $\mathcal{B}$, known as the Borel algebra or Borel $\sigma$-algebra. The Borel $\sigma$-algebra on $X$ is the smallest $\sigma$-algebra containing all open sets (or, equivalently, all closed sets).
关于可数性:
- A set $S$ is said to be countable if it’s finite or $\mathbf{card}(S) = \mathbf{card}(\mathbb{N})$
- $\mathbf{card}(\mathbb{R}) > \mathbf{card}(\mathbb{N})$ (Cantor Diagonal Argument)
- If $\mathcal{B}$ is a Borel algebra in $\mathbb{R}$, then $\mathbf{card}(\mathcal{B}) = \mathbf{card}(\mathbb{R})$
- 结论:$\mathcal{B}$ 不可数
Prerequisite #3 : Measurable Function / Measurable Space
Definition: A measurable space is a tuple of $(S, \Sigma)$ where $S$ is a set and $\Sigma$ is a $\sigma$-algebra over $S$.
- measurable space 又称 Borel space
Definition: Let $(X, \Sigma_X)$ and $(Y, \Sigma_Y)$ be measurable spaces. Function $f:X \to Y$ is called a measurable function if $\forall E_Y \in \Sigma_Y, f^{-1}(E_Y) \in \Sigma_X$
- $f^{-1}$ 是 inverse function
- 扩展一下 $f^{-1}$ 的定义:$f^{-1}(E_Y) := \lbrace x \in X \vert f(x) \in E_Y \rbrace$
- 这个定义相当于:$\forall E_Y \in \Sigma_Y, \exists E_X \in \Sigma_X$ 使得 $f(E_X) = E_Y$
- 这个 $E_X$ 即 $f^{-1}(E_Y)$
- 为了强调 $f$ 是一个 measurable function,我们也可以把它写作 $f: (X, \Sigma_X) \to (Y, \Sigma_Y)$
Prerequisite #4 : Measure / Measure Space
Definition: Let $(S, \Sigma)$ be a measurable space. Function $\mu: \Sigma \to \mathbb{R} \cup \lbrace -\infty, \infty \rbrace$ is called a measure if it satisfies the following properties:
- Non-negativity: $\forall E \in \Sigma, \mu(E) \geq 0$
- 注:不满足这个条件的 measure 是存在的,比如 signed measure
- Null empty set: $\mu(\varnothing) = 0$
- Countable additivity (or $\sigma$-additivity): $\forall \text{ countable collection } \lbrace E_i \rbrace^{\infty}_{i=1}$ where $E_i \in \Sigma, \forall i$ and $E_i \cap E_j = \varnothing, \forall i, j$:
Definition: A measure space is such a triple of $(S, \Sigma, \mu)$
Prerequisite #5 : Probability Measure / Probability Space
Definition: Measure $\mu$ is probability measure if $\mu(S) = 1$.
- $S$ 指全集
Definition: A probability space is a measure space with a probability measure, denoted by $(\Omega, \mathcal{F}, \mathbb{P})$ where:
- $\omega \in \Omega$ is called an outcome
- $E \in \mathcal{F}$ is called an event
- $\mathbb{P}: \mathcal{F} \to [0,1]$ is a probability measure
- $\mathbb{P}(E)$ is the probability of $E$
Prerequisite #3/#4/#5 Summary
- measurable function $f$ 定义在 measurable space $(S, \Sigma)$ 上
- measurable function $f$ 有潜力构成一个 measure $\mu$
- measure $\mu$ + measurable space $(S, \Sigma)$ = measure space $(S, \Sigma, \mu)$
- probability measure $\mathbb{P}$ 是特殊的 measure
- 装备 probability measure 的 measure space 是 probability space $(\Omega, \mathcal{F}, \mathbb{P})$
我们可以把 measurable function $f$ $\overset{\text{进化}}{\Rightarrow}$ measure $\mu$,但注意这里涉及一个定义域转化的问题:
- $f: S \to \mathbb{R}$
- $\mu: \Sigma \to \mathbb{R}$
- 比如我们可以定义 $\mu(\lbrace x \rbrace) = f(x)$ 然后根据 $\sigma$-additivity 有:
- 注意我这里的意思是:我们可以这样做,但没有规定说一定要这样做;$\mu$ 也不一定要通过 $f$ 定义,$f$ 也不一定满足进化成 $\mu$ 的要求
1. Random Variable
Definition: A random variable $X$ is a measurable function $X: (\Omega, \mathcal{F}) \to (\mathbb{R}, \mathcal{B})$ such that $\forall$ Borel set $B\in \mathcal{B}$
\[X^{-1}(B) \overset{\text{informal}}{=} \lbrace X \in B \rbrace = \lbrace \omega \in \Omega \vert X(\omega) \in B \rbrace \in \mathcal{F}\]- 准确来说应该是 $\mathbb{R} \cup \lbrace -\infty, \infty \rbrace$ 而不仅仅是 $\mathbb{R}$
- $\mathcal{B}$ 是 $\mathbb{R}$ 上的 Borel $\sigma$-algebra
若 $X$ 是 $(\Omega, \mathcal{F}, \mathbb{P})$ 上的 random variable,那么:
- 我们称 $X$ 是 $\mathcal{F}$-measurable. We define $\mathcal{F}(X)$ to be the smallest $\sigma$-algebra on $\Omega$ for which $X$ is measurable.
- 比较一下 $X$ 和 $\mathbb{P}$:
- 首先注意定义域:
- $X: \Omega \to \mathbb{R}$ (random variable 接收 outcome)
- $\mathbb{P}: \mathcal{F} \to [0, 1]$ (probability measure 接收 event)
- $X$ 是 measurable function,$\mathbb{P}$ 是 probability measure,我们可以像上面 $f$ $\overset{\text{进化}}{\Rightarrow}$ $\mu$ 一样定义一个 $X$ 使它可以 $X$ $\overset{\text{进化}}{\Rightarrow}$ $\mathbb{P}$,但是!没有必要。后面 distribution 的部分会阐述。
- 首先注意定义域:
以投骰子为例 (一个骰子,仅投一次):
- $\Omega = \lbrace 1,2,3,4,5,6 \rbrace$
- $\mathcal{F}$ 包括但不限于 $\Omega$、$\lbrace 1 \rbrace$、$\lbrace 2 \rbrace$、$\lbrace 3 \rbrace$、$\lbrace 4 \rbrace$、$\lbrace 5 \rbrace$、$\lbrace 6 \rbrace$
- 假设有 $\mathbb{P}(\lbrace 1 \rbrace) = \mathbb{P}(\lbrace 2 \rbrace) = \mathbb{P}(\lbrace 3 \rbrace) = \mathbb{P}(\lbrace 4 \rbrace) = \mathbb{P}(\lbrace 5 \rbrace) = \mathbb{P}(\lbrace 6 \rbrace) = \frac{1}{6}$
- 注意 event $\lbrace 1,3 \rbrace$ 表示 “roll 出 1 或者 3”,而不是 “roll 两次,一次是 1 一次是 3”
- “roll 两次,一次是 1 一次是 3” 的 event 应该是 $\big \lbrace \lbrace 1,3 \rbrace \big \rbrace$
- 所以 $\mathbb{P}(\lbrace 1,3 \rbrace) = \mathbb{P}(\lbrace 1 \rbrace) + \mathbb{P}(\lbrace 3 \rbrace) = \frac{1}{3}$,同理有 $\mathbb{P}(\Omega) = 1$
- “roll 出 1 且 3” 是不可能事件,即 $\varnothing$,由 measure 的定义得到 $\mathbb{P}(\varnothing) = 0$
- 注意 event $\lbrace 1,3 \rbrace$ 表示 “roll 出 1 或者 3”,而不是 “roll 两次,一次是 1 一次是 3”
2. Distribution of a Random Variable
假定有 probability space $(\Omega, \mathcal{F}, \mathbb{P})$,其上有一个 arbitrary 的 random variable $X$.
Definition: The push-forward measure of $\mathbb{P}$ by $X$ is a function $\mathbb{P}_{X}: \mathcal{B} \to \mathbb{R}$ such that $\forall B \in \mathcal{B}$,
\[\mathbb{P}_{X}(B) = \big (\mathbb{P} \circ X^{-1} \big )(B) = \mathbb{P}(X^{-1}(B)) \overset{\text{informal}}{=} \mathbb{P}(\lbrace X \in B \rbrace) = \mathbb{P}(\lbrace \omega \in \Omega \vert X(\omega) \in B \rbrace)\]- 注意根据 random variable 的定义,$\forall B \in \mathcal{B}, X^{-1}(B) \in \mathcal{F}$,所以 $X^{-1}(B)$ 在 $\mathbb{P}$ 的定义域内
- $\mathbb{P}_{X}$ 一定是一个 probability measure,使得 $(\mathbb{R}, \mathcal{B}, \mathbb{P}_{X})$ 构成一个 probability space
- 若 $X = I$,即 $X(\omega) = \omega$,可得 $\mathbb{P}_{X} = \mathbb{P}$
我们称 $\mathbb{P}_{X}$ 为 distribution of random variable $X$.
我们这里重点考察一下 $\mathbb{P}_{X}$ 和 $\mathbb{P}$ 的关系,并引申出 $X$ 在其中的作用:
- $\mathbb{P}: \mathcal{F} \to [0, 1]$
- $X: (\Omega, \mathcal{F}) \to (\mathbb{R}, \mathcal{B})$
- 按理来说,$X^{-1}$ 应该是 $X^{-1}: \mathbb{R} \to \Omega$,但是我们通过 $X^{-1}(B)$ 的定义把它扩展成了 $X^{-1}: \mathcal{B} \to \mathcal{F}$
- 于是 $\mathbb{P}_{X} = \mathbb{P} \circ X^{-1}$ 就成了一个 $\mathcal{B} \to \mathcal{F} \to [0, 1]$ 的函数
- 所以 $X: \mathcal{F} \to \mathcal{B}$ 就可以看作一个 “event encoder“,它把每一个 event $E \in \mathcal{F}$ 映射到一个 Borel set $B \in \mathcal{B}$
- 同理$X^{-1}: \mathcal{B} \to \mathcal{F}$ 就可以看成一个 “event decoder“,它把每一个 Borel set $B \in \mathcal{B}$ 又映射回原来的 event $E \in \mathcal{F}$
- Event encoding 的作用在于:可以把各种不同的、具体的 $(\Omega, \mathcal{F})$ 转化为统一的、抽象的 $(\mathbb{R}, \mathcal{B})$
- 比如 “投骰子” 和 “黑盒子里 6 个不同颜色的球,抓一个出来” 这两个实验,它们的 event 是不一样的,但我们明显可以看出它们的本质是一样的,这个本质体现在它们通过 $X$ encoding 以后,得到的 Borel set 是一样的 (或者说得到的 $\mathbb{P}_X$ 函数是一样的)
- Event decoding 的作用在于计算,因为 $\mathbb{P}_X$ 需要借助 $\mathbb{P}$ 才能算出具体的值
- 我们平时根本就没有注意到这个 event encoding/decoding 的过程是因为:它太顺理成章了。比如上面 “投骰子” 的例子,我们直接就写出了 $\Omega = \lbrace 1,2,3,4,5,6 \rbrace$,所以可以有 $E = B$,亦即 $X = I$,等于没有做 event encoding/decoding,于是我们也没有区分 $\mathbb{P}_{X}$ 和 $\mathbb{P}$,因为 $\mathbb{P}_{X} = \mathbb{P}$
- 但是我也可以定义说 $\Omega = \lbrace \text{I}, \text{II}, \text{III}, \text{IV}, \text{V}, \text{VI}\rbrace$,那你可能需要 encode 一下,得到:
- $X(\text{I}) = 1$
- $\dots$
- $X(\text{VI}) = 6$
- 所以 $\mathbb{P}_{X}(\lbrace 3 \rbrace) = \mathbb{P}(X^{-1}(\lbrace 3 \rbrace)) = \mathbb{P}(\lbrace \text{III} \rbrace)$
- 当然,你的 $X$ 的定义可以不用与 event 的语义对应,比如我定义 $X(\text{I}) = 100, \dots, X(\text{VI}) = 600$,也是可以的
题外话:$\mathbb{P}(X = 3)$ 这种写法如何解释?
- 先说结论:这是个有点过分的简写
- 首先 $\mathbb{P}(X = 3)$ 应该是 $\mathbb{P}(\lbrace X = 3 \rbrace)$ ($\mathbb{P}$ 接收 event)
- 二来 $X = 3$ 应该理解为 $X \in \lbrace 3 \rbrace$
- 这么一来,令 $B = \lbrace 3 \rbrace$,套公式可得:
- 所以 $X = 3$ 整体是一个 event $E \in \mathcal{F}$ (informal);而 $\lbrace 3 \rbrace$ 是一个 Borel set $B \in \mathcal{B}$
- 若 $X = I$,则 $E = B$, $\mathbb{P}_{X} = \mathbb{P}$,从而 $\mathbb{P}(X = 3) \overset{\text{informal}}{=} \mathbb{P}_X(\lbrace 3 \rbrace) = \mathbb{P}(\lbrace 3 \rbrace)$
$\mathbb{P}_{X}$ 的性质还有:
- If $\mathbb{P}_{X}$ gives measure one to a countable set of reals, then $X$ is called a discrete random variable.
- $\mathbb{P}_{X}: \mathcal{B} \to [0, 1]$, 然后 $\mathcal{B}$ 不可数
- 但 $\mathbb{P}_{X}$ 的 domain 可能只是 $\mathcal{B}$ 的一个可数子集
- If $\mathbb{P}_{X}$ gives zero measure to every singleton set, and hence to every countable set, $X$ is called a continuous random variable.
- Every random variable can be written as a sum of a discrete random variable and a continuous random variable.
- All random variables defined on a discrete probability space are discrete
Definition: 对任意的 (locally finite) measure $\mu$ on $\mathbb{R}$,我们定义 distribution function of $\mu$ as
\[F_{\mu}(x) = \mu \big ( (-\infty, x] \big)\]那既然 $\mathbb{P}_{X}$ 是一个 probability measure (probability measure 一定是 locally finite),我们可以定义:
\[F_{\mathbb{P}_{X}}(a) = \mathbb{P}_{X} \big ( (-\infty, a] \big) = \mathbb{P} \Big ( X^{-1}\big ( (-\infty, a] \big) \Big) \overset{\text{informal}}{=} \mathbb{P}\big ( \lbrace X \in (-\infty, a] \rbrace \big ) \overset{\text{informal}}{=} \mathbb{P}(X \leq a)\]严格来说,$F_{\mathbb{P}_{X}}$ 应该叫做 distribution function of the distribution of random variable $X$,但是非常不幸的是,它也被简称为 distribution of random variable $X$,并且简化符号为 $F_X = F_{\mathbb{P}_{X}}$
3. Probability Mass Functions (for the discrete), and Probability Density Functions (for the continuous)
Definition: Probability mass function for discrete random variable $X$, $p_X: \mathbb{R} \to [0, 1]$, can be defined as:
\[\begin{aligned} p_X(x) &= \mathbb{P}(X = x) = \mathbb{P}_X(\lbrace x \rbrace) \newline \sum_{x \in \mathbb{R}} p_X(x) &= 1 \end{aligned}\]其实就是把 $\mathbb{P}_X$ 的定义域中的 one-element $B \in \mathcal{B}$ 的部分降维到了 $x \in \mathbb{R}$,就是这么简单。
Definition: Probability density function for continuous random variable $X$, $f_X: \mathbb{R} \to [0, \infty)$, is one satisfying:
\[\begin{aligned} \int_{a}^{b} f_X(x) \mathrm{d}x &= \mathbb{P} \big ( \lbrace a \leq X \leq b \rbrace \big ) = F_X(b) - F_X(a) \newline \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} f_X(x) \mathrm{d}x &= 1 \end{aligned}\]- 严格来说,$f_X$ 应该叫做 “the density or Radon–Nikodym derivative with respect to Lebesgue measure of random variable $X$”
若 $f_X$ 存在:
- 我们可以写 $F_X(x) = \int_{-\infty}^{x} f_X(t) \mathrm{d}t$
- If $f_X$ is continuous at $t \Rightarrow f_X(x) = F_X’(x)$
4. Tilde $\sim$ / i.i.d.
根据 Ben O’Neill: Why are probability distributions denoted with a tilde?,$\sim$ 其实是一个 equivalence relation,所以 $X \sim Y$ 左右两边都是 random variable,它可以念做 “$X$ has the same distribution as $Y$”。我觉得这基本就是 $X = Y$ 的意思了。
- 所以 $\mathcal{N}(0, 1)$ 它不是 distribution,而是一个 random variable
- 如果 $X \sim \mathcal{N}(0, 1)$,那么 $X(x) = \mathcal{N}(x; 0, 1)$
- 如果 $\mu, \sigma^2$ 不确定,$\mathcal{N}(\mu, \sigma^2)$ 可以看做一个 parametric random variable
- 注意如果有 $X \sim \mathcal{N}(\mu, \sigma^2)$,那么这里 $\mathcal{N}(\mu, \sigma^2)$ 一定是表示一个具体的 random variable (once $\mu, \sigma^2$ 确定下来),而不能理解为是一个 family of random variables
那么问题来了:”has the same distribution as” 这个 distribution 指的是 $\mathbb{P}_{X}$ 还是 $F_X = F_{\mathbb{P}_{X}}$?
- 若 $X \sim Y$ 都是 discrete random variable,那么明显 $\mathbb{P}_{X}$ 更直接,所以一般我们用 $\mathbb{P}_{X} = \mathbb{P}_{Y}$ 这个结论
- 进而有 $p_X = p_Y$
- 若 $X \sim Y$ 都是 continuous random variable,那么明显 $F_X$ 才有意义,所以一般我们用 $F_X = F_Y$ 这个结论
- 进而有 $f_X = f_Y$
我们直接研究 random variable $X$ 即意味着我们跳过了 event encoding/decoding 的步骤,直接在 $(\mathbb{R}, \mathcal{B}, \mathbb{P}_{X})$ 这个抽象的 probability space 上工作,至于原来的 $(\Omega, \mathcal{F}, \mathbb{P})$ 长什么样子我们就不关心了。
另外还有一个常见的概念是 i.i.d. (independent and identically distributed),它是用来形容一组 random variables 的。简单说,如果 $X_1, \dots , X_n$ 是一组 i.i.d. 的 random variables,那么:
- $X_1 \sim X_2 \sim \dots X_{n-1} \sim X_n$ (我觉得诡异的是这么多年我就没见过哪本教材用这个式子来描述 i.i.d.)
- $X_1, \dots , X_n$ 互相是 independent 的
5. Independence / Marginal Distribution / Join Distribution
我们先从 $(\Omega, \mathcal{F}, \mathbb{P})$ 的层次入手。
Definition: (1) Two events $E_1, E_2$ are called independent if
\[\mathbb{P}(E_1 \cap E_2) = \mathbb{P}(E_1) \mathbb{P}(E_2)\](2) A collection of events $\lbrace E_i \rbrace$ is called independent if $\forall$ distinct $E_1, \dots, E_n$,
\[\mathbb{P}(E_1 \cap \dots \cap E_n) = \mathbb{P}(E_1) \dots \mathbb{P}(E_n)\](3) A collection of events $\lbrace E_i \rbrace$ is called pairwise independent if $\forall$ distinct $E_i, E_j$,
\[\mathbb{P}(E_i \cap E_j) = \mathbb{P}(E_i) \mathbb{P}(E_j)\](4) A finite collection of $\sigma$-algebras $\mathcal{F}_1, \dots, \mathcal{F}_n$ is called independent if $\forall$ $E_1 \in \mathcal{F}_1, \dots, E_n \in \mathcal{F}_n$, $\lbrace E_1, \dots, E_n \rbrace$ is independent.
(5) An infinite collection of $\sigma$-algebras is called independent if every subcollection is independent.
If $X_1, \dots , X_n$ are random variables, we can consider them as a random vector $(X_1, \dots , X_n)$ and hence as ONE random variable $X_{1:n}: \mathcal{B(\mathbb{R}^n)} \to \mathbb{R}^n$
- Let $\mathcal{T}(\mathbb{R}^n) \subset \mathcal{P}(\mathbb{R}^n)$ denote the standard topology on $\mathbb{R}^n$ consisting of all open sets
- $\mathcal{P}(S) = 2^S$
- $\mathcal{B(\mathbb{R}^n)}$ is the $\sigma$-algebra generated by all the open set, i.e. $\mathcal{B(\mathbb{R}^n)} = \sigma \big ( \mathcal{T}(\mathbb{R}^n) \big )$
假设原有 probability spaces $(\Omega_1, \mathcal{F}_1, \mathbb{P}_1), \dots, (\Omega_n, \mathcal{F}_n, \mathbb{P}_n)$,令 $\Omega_{1:n} = \Omega_1 \times \dots \times \Omega_n$, $\mathcal{F}_{1:n} = \mathcal{F}_1 \otimes \dots \otimes \mathcal{F}_n$, $\mathbb{P}_{1:n} = \mathbb{P}_1 \times \dots \times \mathbb{P}_n$. 注意,根据 Wikipedia: Product measure:
- $\Omega_1 \times \Omega_2$ is the Cartesian product of the two sets
- $\mathcal{F}_1 \otimes \mathcal{F}_2$ is the $\sigma$-algebra on $\Omega_1 \times \Omega_2$, generated by subsets of the form $E_{1} \times E_{2}$ where $E_{1} \in \mathcal{F}_{1}$ and $E_{2} \in \mathcal{F}_{2}$
- A product measure $\mathbb{P}_1 \times \mathbb{P}_2$ is defined to be a measure on the measurable space $(\Omega_1 \times \Omega_2, \mathcal{F}_1 \otimes \mathcal{F}_2)$ satisfying $\forall E_{1} \in \mathcal{F}_{1}, \forall E_{2} \in \mathcal{F}_{2}$,
假设 $X_1$ 是 $(\Omega_1, \mathcal{F}_1, \mathbb{P}_1)$ 上的 random variable,$\dots$,$X_n$ 是 $(\Omega_n, \mathcal{F}_n, \mathbb{P}_n)$ 上的 random variable。然后我们有一批:
- distribution: $\mathbb{P}_{X_1}, \dots, \mathbb{P}_{X_n}$
- distribution function of distribution: $F_{X_1}, \dots, F_{X_n}$
- PMF: $p_{X_1}, \dots, p_{X_n}$
- PDF: $f_{X_1}, \dots, f_{X_n}$
Definition: For random variable $X_{1:n} = (X_1, \dots , X_n)$, its joint distribution $\mathbb{P}_{X_{1:n}}: \mathcal{B(\mathbb{R}^n)} \to \mathbb{R}$ can be defined as: $\forall B_{1:n} = B_1 \times \dots \times B_n$, $B_{1:n} \in \mathcal{B(\mathbb{R}^n)}$
\[\mathbb{P}_{X_{1:n}}(B_{1:n}) = \mathbb{P}_{1:n} \big (X_{1:n}^{-1}(B_{1:n}) \big) \overset{\text{informal}}{=} \mathbb{P}_{1:n} \big ( \lbrace X_{1:n} \in B_{1:n} \rbrace \big ) \overset{\text{informal}}{=} \mathbb{P}_{1:n} \big ( \lbrace X_1 \in B_1, \dots, X_n \in B_n \rbrace \big )\]Definition: For joint distribution $\mathbb{P}_{X_{1:n}}$, its joint distrbution function $F_{X_{1:n}} \overset{\text{abbrev.}}{=} F_{\mathbb{P}_{X_{1:n}}}: \mathbb{R}^n \to [0, 1]$ can be defined as: $\forall t_i \in \mathbb{R}$
\[F_{X_{1:n}}(t_1, \dots, t_n) \overset{\text{informal}}{=} \mathbb{P}_{1:n} \big ( \lbrace X_1 \leq t_1, \dots, X_n \leq t_n \rbrace \big ) = \mathbb{P}_{X_{1:n}} \big ( (-\infty, t_1] \times \dots \times (-\infty, t_n] \big )\]Definition: For random variable $X_{1:n} = (X_1, \dots , X_n)$, its joint probability mass function $p_{X_{1:n}}: \mathbb{R}^n \to [0, 1]$ can be defined as:
\[\begin{aligned} p_{X_{1:n}}(x_1, \dots, x_n) &= \mathbb{P}_{X_{1:n}} \Big ( \big \lbrace \lbrace x_1, \dots, x_n \rbrace \big \rbrace \Big ) = \mathbb{P}_{1:n}(\lbrace x_1, \dots, x_n \rbrace) \newline \sum_{\vec x \in \mathbb{R}^n} p_{X_{1:n}}(\vec x) &= 1 \end{aligned}\]Definition: For random variable $X_{1:n} = (X_1, \dots , X_n)$, its joint probability density function $f_{X_{1:n}}: \mathbb{R}^n \to [0, \infty]$ is one statisfying: $\forall B_{1:n} = B_1 \times \dots \times B_n, B_{1:n} \in \mathcal{B(\mathbb{R}^n)}$,
\[\begin{aligned} \int_{B_{1:n}} f_{X_{1:n}}(x_1, \dots, x_n) \mathrm{d}x_1 \dots \mathrm{d}x_n &= \mathbb{P}_{X_{1:n}}(B_{1:n}) \newline \int_{\mathcal{B(\mathbb{R}^n)}} f_{X_{1:n}}(x_1, \dots, x_n) \mathrm{d}x_1 \dots \mathrm{d}x_n &= 1 \end{aligned}\]Definition: Random variables $X_1, \dots, X_n$ are said to be independent if any of these (equivalent) conditions hold:
(1) Joint distribution is the product of all marginal distributions:
\[\begin{aligned} \mathbb{P}_{X_{1:n}}(B_{1:n}) \overset{\text{informal}}{=} & \mathbb{P}_{1:n} \big ( \lbrace X_1 \in B_1, \dots, X_n \in B_n \rbrace \big ) \newline = &\mathbb{P}_{1}(\lbrace X_1 \in B_1 \rbrace) \dots \mathbb{P}_{n}(\lbrace X_n \in B_n \rbrace) \newline = &\mathbb{P}_{X_1}(B_1) \dots \mathbb{P}_{X_n}(B_n) \end{aligned}\]- This is equivalent of saying “joint distribution is the product measure of all marginal distributions”:
- Marginal distribution of $X$ 其实就是 $X$’s individual distribution,它只在 joint distribution 这个 context 下有意义。语出二维的 discrete joint distribution table,比如:
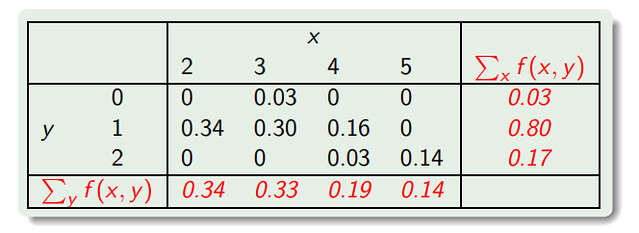
(2) Joint distribution function is the product of all marginal distribution functions:
\[\begin{aligned} F_{X_{1:n}}(t_1, \dots, t_n) &= \mathbb{P}_{X_{1:n}} \big ( (-\infty, t_1] \times \dots \times (-\infty, t_n] \big ) \newline &= \mathbb{P}_{X_1} \big ( (-\infty, t_1] \big ) \dots \mathbb{P}_{X_n} \big ( (-\infty, t_n] \big ) \newline &= F_{X_1}(t_1) \dots F_{X_n}(t_n) \end{aligned}\](3) Joint PMF is the product of all individual PMFs:
\[\begin{aligned} p_{X_{1:n}}(x_1, \dots, x_n) &= \mathbb{P}_{X_{1:n}} \Big ( \big \lbrace \lbrace x_1, \dots, x_n \rbrace \big \rbrace \Big ) \newline &= \mathbb{P}_{X_1} \big ( \lbrace x_1 \rbrace \big ) \dots \mathbb{P}_{X_n} \big ( \lbrace x_n \rbrace \big ) \newline &= p_{X_1}(x_1) \dots p_{X_n}(x_n) \end{aligned}\](4) Joint PDF (if exists) is the product of all individual PDFs:
\[f_{X_{1:n}}(x_1, \dots, x_n) = f_{X_1}(x_1) \dots f_{X_n}(x_n)\](5) The $\sigma$-algebras $\mathcal{F}(X_1), \dots \mathcal{F}(X_n)$ are independent.
6. Conditional Random Variable
Suppse $X, Y$ are discrete random variables over $(\Omega, \mathcal{F}, \mathbb{P})$. If $\mathbb{P}(Y = y) \neq 0$, then we can define the conditional probability (measure):
\[\mathbb{P}(X = x \mid Y = y) = \frac{\mathbb{P}(X = x \text{ and } Y = y)}{\mathbb{P}(Y = y)}\]Definition: The discrete conditional random variable $X \mid Y = y$, read “$X$ given $Y = y$”, has PMF
\[p_{X \mid Y = y}(x) = \mathbb{P} \big ( (X \mid Y = y) = x \big ) = \mathbb{P}(X = x \mid Y = y)\]Similarly, we can have
Definition: The continuous conditional random variable $X \mid Y = y$, has PDF
\[f_{X \mid Y = y}(x) = \frac{f_{X, Y}(x, y)}{f_Y(y)}\]
留下评论