Terminology Recap: SNP / SNV / LD / GWAS / eQTL / DNA Microarray (DNA chip)
1. SNP
SNP == Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism
我们先看下什么叫 gene polymorphism:
- 宽泛地讲,genetic variation refers to diversity in gene frequencies (of different individuals in a population).
- 给 genetic variation 加一个 frequency 的限定,就得到 gene polymorphism: Genetic alterations that occur in more than 1 percent of the population are called polymorphisms.
- 这个定义的意思就是说:太 rare 的 variation (比如你特地辐射一个) 我们就不考虑了
- 那这个 variation 并没有限定说是变几个 nucleotide,变几个都有可能,都算是 variation。那我们再限定是单个 nucleotide 上的 variation,那就成了 SNP
注意:
- SNP 的定义里并没有一个字提到了 trait,所以 SNP 不一定非要和 trait 有关系
- 如果一个 SNP 是 coding SNP (located in CDS or more precisely, exons),那它可能会影响 trait
- 因为它的 alleles 可能对应不同的 aa;此时称这个 SNP 为 non-synonymous SNP (从 codon 的角度看)
- 反之如果 alleles 对应相同的 aa,则称这个 SNP 为 synonymous SNP
- 如果一个 SNP 不是 coding SNP,但如果它可以影响 gene regulation,那它也可能会影响 trait
- 注意 coding SNP 也可能会影响 regulation,比如说一个 SNP 它是 non-synonymous SNP,但是它对应一个 aa 构成了 TF,另一个 aa 无法构成 TF,然后这个 TF 参与了 regulation。这么一个七拐八绕的关系应该也算是影响了 regulation
- 如果一个 SNP 既不是 coding SNP 也不是 regulatory SNP,我想不出什么途径它可以影响 trait
- 你可能会问那这个 SNP 它 vary 一下的意义何在?这是一个值得研究的问题……
另外提到了 trait,多说一句:trait 是 tissue/cell-type specific,比如 eye color == blue 这个 trait 你只可能在 eye cells 中体现。若假设 SNP s 对这个 trait 有 regulation 的影响,它也只能是在 eye cell 中影响 regulation。在其他的 tissue/cell 中,s 应该没有作用 (这应该是由细胞分化和更高层的 gene regulation 决定机制控制的)。
2. SNV
- SNP == Single-Nucleotide (Gene) Polymorphism
- SNV == Single-Nucleotide (Genetic) Variation
所以 SNP 与 SNV 的区别也就是 gene polymorphism 与 genetic variation 的区别:一个有 frequency 的限制,一个没有
3. LD
YouTube: Recombination and linkage disequilibrium:
Linkage disequilibrium (LD): a specific allele at the first locus is associated with a specific allele at the second locus more often than expected by chance.
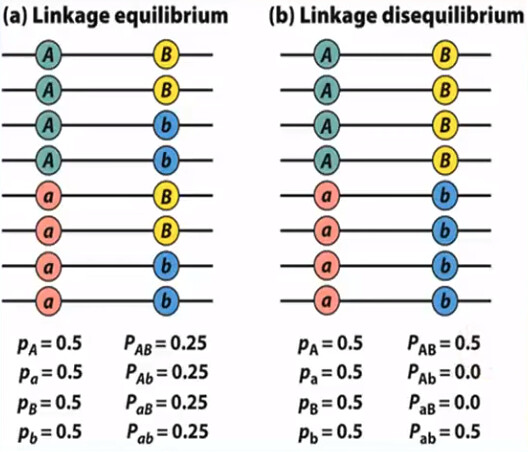
- 所以 LD 其实是一个 scenario,它涉及到两个 locus/gene/SNP (假设为 $s_1$ 和 $s_2$),这两个 locus/gene/SNP 的 4 个 allele (先假设它有 4 个;$s_{1A}$, $s_{1a}$, $s_{2B}$, $s_{2b}$) 的 4 种组合 ($s_{1A} + s_{2B}$, $s_{1A} + s_{2b}$, $s_{1a} + s_{2B}$, $s_{1a} + s_{2b}$) 在 population 中的 frequency 并不是平均的 25%, 25%, 25%, 25%
- 从统计的角度来说:LD 意味 genotype at $s_1$ is dependent of genotype at $s_2$
- 亦即 alleles are not randomly inherited
- 反过来,Linkage equilibrium 则意味着 genotype at $s_1$ is independent of genotype at $s_2$
- 具体在计算时,有一个 coefficient of LD (记做 $D$),有点类似方差 (among genotype frequencies) 的概念 (参考 Linkage disequilibrium and recombination)
- $D \rightarrow 0$ 可以理解为:方差很小,意味着 frequencies 的差别很小
4. GWAS
GWAS == Genome-Wide Association Study
- Aims to find:
- Genetic Variant $\overset{\text{association}}{\longleftrightarrow}$ Trait
- 这里 association 是 statistical 意义上的 association,比如有 correlation
那 SNP 是一种特殊的 genetic variant,也可能会影响 trait,所以 SNP 自然是 GWAS 的研究对象之一。
5. eQTL
eQTL = Expression Quantitative Trait Loci
5.1 QT
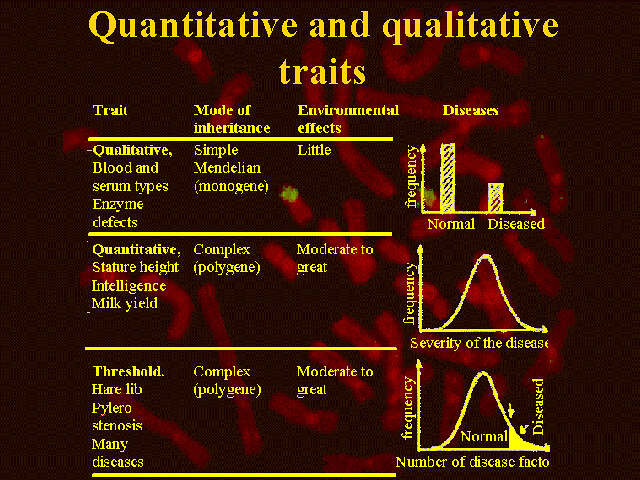
我们先看下什么叫 quantitative trait (source):
A qualitative trait is expressed qualitatively, which means that the phenotype falls into different categories. These categories do not necessarily have a certain order. The pattern of inheritance for a qualitative trait is typically monogenetic, which means that the trait is only influenced by a single gene. Inherited diseases caused by single mutations are good examples of qualitative traits. Another is blood type. The environment has very little influence on the phenotype of these traits.
A quantitative trait shows continued variation. This is because the trait is the sum of several small effects caused by the gene. An example of this is an animal’s metabolism, which is under the influence of many different genes. The final products of the metabolism, as for instance milk yield or growth rate, are good examples of quantitative traits. If several small gene effects are present, the phenotype values for a population will typically have a normal distribution.
In some cases the phenotype values are not distributed normally, even though the trait has a polygenetic inheritance. Traits, which only show a few classes, are called threshold traits.
Consider a continued genotypic distribution. When a threshold is crossed, the phenotype will jump onto another level. It passes from one category to another, or from one phenotype to another. An example of a threshold trait is mastitis in dairy cows. The inheritance is polygenetic, but the only thing that can be recorded is whether a cow contains the disease or not, not at which point on the continued normal distribution it should be recorded.
5.2 QTL
那么接下来,QTL 是指 (source):
A quantitative trait locus (QTL) is a locus (section of DNA) which correlates with variation of a quantitative trait in the phenotype of a population of organisms. QTLs are mapped by identifying which molecular markers (such as SNPs or AFLPs) correlate with an observed trait.
- Wikipedia 这个概念讲得很含蓄,它只说了是 “correlate”,这个 locus 具体是 coding 还是 regulatory 都有可能
- AFLP 指 Amplified Fragment Length Polymophism,具体可以参考 YouTube: PCR Genotyping
classical QTL analysis 的过程大概是这样的 (source):
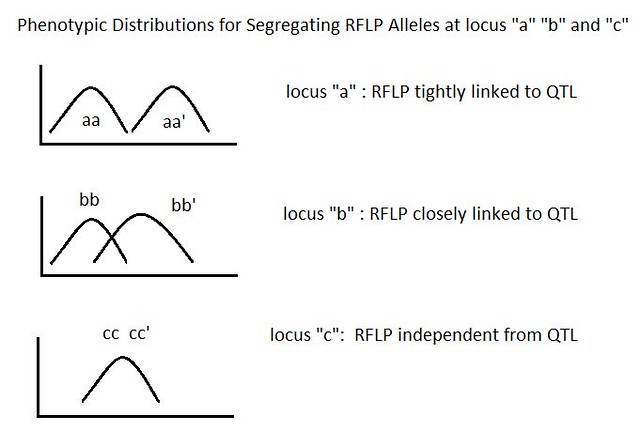
- x-axis 是 trait (因为是 quantitative 所以才能这么量化) (i.e. phenotype)
- y-axis 是 population 中 genotype 的数量
5.3 eQTL
我觉得关于 eQTL 最简练的解释,来自 YouTube: MIT CompBio Lecture 15 - eQTLs 的开头:
… expression QTLs, …, where the quantitative trait is expression.
- 我觉得这解释了为什么 eQTL 不缩写成 EQTL,因为 EQT 这个说法解释不通 (但是为何不缩写成 QEL?)
那么 gene expression 如何量化呢?其中一个手段是 YouTube: DNA microarrays (一个更详细的介绍是 YouTube: DNA Microarray Methodology)。这一大类的量化 gene expression 的手段,我们统称为 Gene Expression Profiling
- DNA Microarray 又叫 DNA Chip
从研究的层次上来看:
- QTL: Locus $\overset{\text{correlates}}{\longrightarrow}$ Quantitative Trait
- eQTL: Locus $\overset{\text{correlates}}{\longrightarrow}$ (Quantitative) Gene Expression $\overset{\text{affects}}{\longrightarrow}$ Trait
eQTL 作为和 trait 有关的 locus,自然也是 GWAS 的研究对象。
Digression: DNA Microarray $\in$ Transcriptome Profiling
所以今后看到 profiling 就应该知道它指的是一大类的方法。Transcriptome Profiling 就是量化 transcriptome (the sum total of all the messenger RNA molecules expressed from the genes of an organism) 的手段。那 DNA Microarray 能量化 gene expression,那是自然也能量化 transcriptome 的。
留下评论