Kernel in Linear Algebra / Quotient space / Isomorphism / Inner Product Space / Hyperplane / SVM / Kernel Function / Normed Vector Space / Metric Space
Kernel in Linear Algebra: Part 1
在 Chapter 6, Digest of Essence of Linear Algebra 有讲:
The null space of matrix $A$ is the set of all vectors $\vec v$ such that $A \vec v = \vec 0$
这里我们用函数的观点展开讲一讲。
Wikipedia: Kernel (linear algebra): The kernel (also known as null space or nullspace) of a linear map (i.e. linear transformation) $L : V \rightarrow W$ between two vector spaces $V$ and $W$, is the set of all elements $\mathbf{v}$ of $V$ for which $L(\mathbf{v}) = \mathbf{0}$, where $\mathbf{0}$ denotes the zero vector in $W$. That is, in set-builder notation,
\[\newcommand{\icol}[1]{ \bigl[ \begin{smallmatrix} #1 \end{smallmatrix} \bigr] } \newcommand{\irow}[1]{ \begin{smallmatrix}(#1)\end{smallmatrix} } \ker(L)=\left \{ \mathbf{v} \in V \mid L(\mathbf{v} ) = \mathbf{0} \right \}\]$\blacksquare$
A linear map is essentially a function,so we can define:
- $L(\mathbf{v}) \in W$ is the image of $\mathbf{v} \in V$
- The image of $L$ is $\mathrm{im}(L) = \left \{ L(\mathbf{v}) \mid \mathbf{v} \in V \right \}$ (所以 $\mathrm{im}(L)$ 是 $W$ 的子空间)
Two elements of $V$ have the same image in $W$ if and only if their difference lies in the kernel of $L$:
\[L(\mathbf{v}_{1}) = L(\mathbf{v}_{2}) \Leftrightarrow L(\mathbf{v}_{1} - \mathbf{v}_{2}) = \mathbf{0}\]The image of $L$ is isomorphic to the quotient of $V$ by the kernel, i.e.:
\[\mathrm{im}(L) \cong V / \ker(L)\]- In linear algebra, the quotient ([ˈkwəʊʃənt], 商) of a vector space $V$ by a subspace $N$ is a vector space obtained by “collapsing” $N$ to zero. The space obtained is called a quotient space and is denoted $V/N$ (read $V$ mod $N$ or $V$ by $N$).
- Morphism refers to a structure-preserving map from one mathematical structure to another.
- 这里的 structure 指的是 Elementary Algebraic Structures 这类的概念
- structure-preserving 的意思就是你的 map $f: X \to Y$ 得到的 $Y$ 必须要保持 $X$ 的 structure,i.e. 若 $X$ 是 field,那么你的 $Y$ 也必须是 field, etc.
- Isomorphism is a morphism that can be reversed by an inverse morphism (just like bijection)
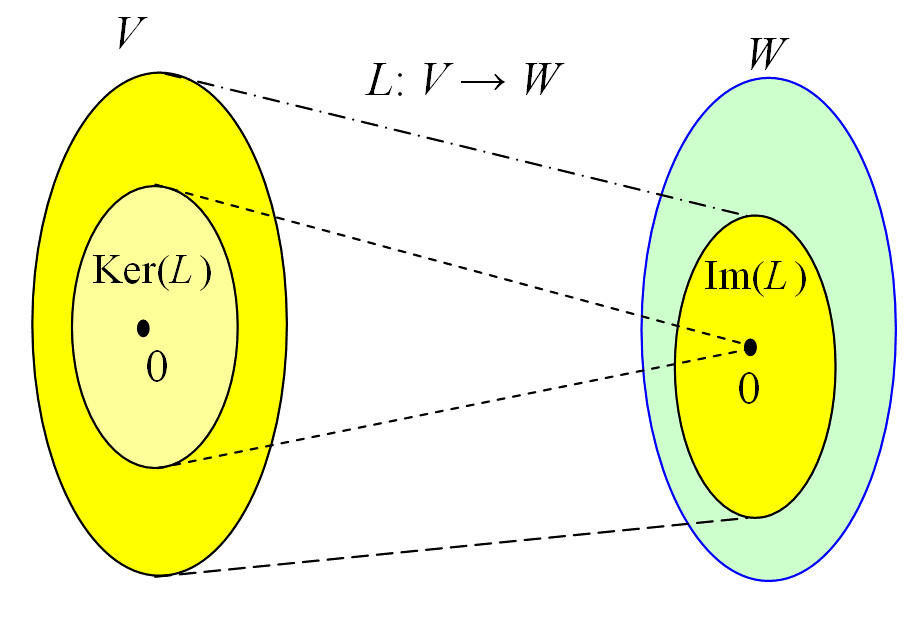
This implies the rank–nullity theorem:
\[\dim(\ker(L)) + \dim(\mathrm{im}(L)) = \dim(V)\]where, by rank we mean the dimension of $\mathrm{im}(L)$, and by nullity that of $\ker(L)$.
- vector space 的 demension 即 basis vector 的个数
举个例子:
- $V = \left \{ \icol{x \newline y} \mid x^2 + y^2 = 1 \right \}$
- $W = \mathbb{R}$
- $L(\mathbf{v}) = A \mathbf{v} = \icol{1 & 0} \icol{x \newline y} = x$
- 相当于把 $x^2 + y^2 = 1$ 这个圆压扁到 x-axis
- $\ker(L)=\left \{ \mathbf{v} \in V \mid \mathbf{v} = \icol{0 \newline y} \right \}$,即 y-axis 上的所有 vector
- $\mathrm{im}(L) = \left \{ x \mid -1 \le x \le 1 \right \}$
- $\dim(\ker(L)) = 1, \, \dim(\mathrm{im}(L)) = 1, \, \dim(V) = 2$
Inner Product Space
Given a vector space $V$ on a field $K$, an inner product between the vectors $\mathbf{v}$ and $\mathbf{w}$ in $V$, which we denote by the symbol $\langle \mathbf{v}, \mathbf{w} \rangle$, is any operation of $V \times V \rightarrow K$ such that the following three properties are satisfied for every $\mathbf{u}, \mathbf{v}, \mathbf{w} \in V$ and for every $a, b \in K$:
- (Positivity or Positive Definiteness):
- $\langle \mathbf{v}, \mathbf{v} \rangle \ge 0$
- $\langle \mathbf{v}, \mathbf{v} \rangle = 0 \iff \mathbf{v} = \mathbf{0}$
- (Linearity): $\langle a\mathbf{v} + b\mathbf{v}, \mathbf{w} \rangle = a\langle \mathbf{u}, \mathbf{w} \rangle + b\langle \mathbf{v}, \mathbf{w} \rangle$
- (Conjugate Symmetry): $\langle \mathbf{u}, \mathbf{v} \rangle = \langle \mathbf{v}, \mathbf{u} \rangle$
- conjugate 这个词的意义有很多,比如:
- $x - y$ 是 $x + y$ 的 conjugate
- $a - b\mathrm{i}$ 是 $a + b\mathrm{i}$ 的 conjugate
- $F=Y^{-1}GY$ 是 $G$ 的 conjugate
- conjugate 这个词的意义有很多,比如:
很多地方把 inner product 这个 operation 写作 $\langle \cdot,\cdot \rangle$,它本质就是个 function $f(\cdot, \cdot) = \langle \cdot,\cdot \rangle$。另外一个很烦人的地方是,inner product 你得结合语境去判断它到底是指的 $\langle \mathbf{v}, \mathbf{w} \rangle$ 这个具体值还是 $\langle \cdot,\cdot \rangle$ 这个 operation。
从 inner product 的定义来看,dot product 是 inner product 的一种,即 dot product 可以通过 inner product 定义:$\langle \mathbf{v}, \mathbf{w} \rangle = \mathbf{v} \cdot \mathbf{w}$
我们知道 Vector space 的定义就是 vector 的集合以及定义在 vector 上的 add、multiply 的操作;如果我们在 vector space 的基础上再加上一个 $\langle \cdot,\cdot \rangle$ 操作,我们就可以得到一个 inner product space。
Two vectors of an inner product space are orthogonal if and only if their inner product is zero.
If $V$ is an inner product space, and $W$ is a subspace of $V$, we define the orthogonal complement of $W$, which we denote by $W^{\bot}$, as the set of all the vectors of $V$ that are orthogonal to every vector of $W$:
\[W^{\bot} = \left \{ \mathbf{v} \in V \mid \langle \mathbf{v}, \mathbf{w} \rangle = 0, \, \forall \mathbf{w} \in W \right \}\]Kernel in Linear Algebra: Part 2
Lemma: Let $A: V \rightarrow W$ be a linear transformation of finite-dimensional vector spaces. Then
\[\mathrm{im}(A^{T}) = (\ker(A))^{\bot}\]Proof:
注意:
- 如果有 $A: V \rightarrow W$,那么 $A^T$ 就是个 $W \rightarrow V$ 的 linear transformation
- 这里 inner product 其实就是 dot product 了
- 这个其实可以扩展到任意的 linear operator $A$,只是不用 $A^{T}$ 而是 adjoint $A^{\ast}$ 来表示逆运算
If $\mathbf{v} \in \mathrm{im}(A^{T}) \subset V$, then $\mathbf{v} = A^{T} \mathbf{w}$ for some $\mathbf{w} \in W$. Now given $\mathbf{u} \in \ker(A)$, then $A \mathbf{u} = \mathbf{0}$. Therefore,
\[\langle \mathbf{u}, \mathbf{v} \rangle = \mathbf{u} \cdot A^{T} \mathbf{w} = A \mathbf{u} \cdot AA^{T} \mathbf{w} = \mathbf{0} \cdot \mathbf{w} = 0\]That is $\mathbf{v} \in (\ker(A))^{\bot}$. 后续证明暂略。感觉直接证 adjoint 更简单……
Hyperplane
Let $\mathrm{R}^n$ be an $n$-dimension vector space and $\mathbf{a} = (a_1, a_2, \dots, a_n)$. $\left \{ a_i \right \}$ are scalars not all equal to 0. Then the set $S = \left \{ \mathbf{x} \in \mathrm{R}^n \mid \mathbf{a} \cdot \mathbf{x} = b \right \}$, where $b$ is a constant, is a subspace of $\mathrm{R}^n$ called a hyperplane.
注意 $\mathbf{a} = (a_1, a_2, \dots, a_n)$ 这个变换并没有 preserve 原点,所以它不是一个严格的 linear transformation 而是一个 affine transformation。然后 hyperplane 可以看作是这个 affine transformation $A(\mathbf{x}) = \mathbf{a} \cdot \mathbf{x} - b$ 的 kernel。
Hyperplane 的 normal vector 可以由 transformation 的 gradient 给出:$\mathbf{n} = \nabla A(\mathbf{x})$,刚好有 $\nabla A(\mathbf{x}) = \mathbf{a}$,所以 hyperplane 的 normal vector $\mathbf{n} = \mathbf{a}$
Normal vector 的性质是它垂直于 hyperplane。
对任意 vector $\mathbf{x}$,当 hyperplane 经过原点时,$\mathbf{x}$ 到 hyperplane 的距离等于它到 normal vector 的投影的绝对值,所以有:
\[D(\mathbf{x}) = \left | \frac{\mathbf{a} \cdot \mathbf{x}}{\vert \mathbf{a} \vert } \right |\]若 hyperplane 不经过原点,我们取 hyperplane 上的任意一点 $p$,原点到 $p$ 的向量为 $\vec{op}$。我们把 $\mathbf{x}$ 写作 $\vec{ox}$,所以 $\vec{px} = \vec{ox} - \vec{op}$ 到 normal vector 的投影的绝对值才是 $\mathbf{x}$ 到 hyperplane 的距离。又因为 $p$ 在 hyperplane 上,所以 $\mathbf{a} \cdot \vec{op} = b$,所以:
\[D(\mathbf{x}) = \left | \frac{\mathbf{a} \cdot (\vec{ox} - \vec{op})}{\vert \mathbf{a} \vert } \right | = \left | \frac{\mathbf{a} \cdot \mathbf{x} - b}{\vert \mathbf{a} \vert } \right |\]注意这里有一个很重要的思想:当 hyperplane 过原点时,我们很容易错误地认为 hyperplane 是 hyperplane 上所有 vector 的集合;从 hyperplane 不经过原点的情况来看,正确的理解应该是:hyperplane 是所有从原点出发、落到 hyperplane 上的 vector 的终点的集合。扩展开来,所谓 “vector 张成的空间”,指的就是 “所有 vector 的终点所构成的空间”
造成这个误解的原因在于我混淆了 hyperplane 在几何学和集合论中的意义:
- 几何学中,hyperplane 是个平面(假设 3-D 情况下)
- 集合论中,hyperplane 是 vector 的集合(vector space)
- 我们说 vector $\mathbf{v} \in H$, where $H$ is a hyperplane,并不是说在几何学中,整个 vector $\mathbf{v}$ 都在 $H$ 这个平面之中,而是说 $\mathbf{v}$ 从原点出发,终点会落在 $H$ 这个平面之中
基于这个思想,我们还应该认识到:
- (几何学)Hyperplane 平面上没有 vector,只有 vector 的终点;只是当 hyperplane 平面经过原点时,它恰巧包含 vector
- (几何学)从原点出发,终点落到 hyperplane 平面上的 vector $\mathbf{x}$ 才满足 $A(\mathbf{x}) = \mathbf{a} \cdot \mathbf{x} - b = 0$,并不是 hyperplane 平面上的 vector 满足 $A(\mathbf{x}) = \mathbf{a} \cdot \mathbf{x} - b = 0$
- (集合论)Hyperplane 这个 vector space 内的所有 vector $\mathbf{x}$ 满足 $A(\mathbf{x}) = \mathbf{a} \cdot \mathbf{x} - b = 0$
- (几何学)Normal vector 垂直于 hyperplane 平面,并不是说 Normal vector 垂直于 hyperplane 平面上的所有 vector
- (集合论)Normal vector 也并不垂直于 hyperplane 这个 vector space 内的所有 vector(除非 hyperplane 经过原点)
- (几何学)我们可以把 原点 + hyperplane 平面 的整体结构想象成一个底面积无限大的圆锥:
- 顶点是原点
- 底是 hyperplane 平面
- 顶点到底面任意一点的连线都是 vector
- 顶点到底面几何中心的连线是一个 normal vector
- 这个 normal vector 的长度,即圆锥的高是 $\left | \frac{b}{\vert \mathbf{a} \vert } \right |$
- 这个 normal vector 不一定是 $\mathbf{a}$,但一定与 $\mathbf{a}$ 共线
- 换言之 $\mathbf{a}$ 不一定落在 hyperplane 平面上
- 再换言之 $\mathbf{a}$ 相当于是从原点出发的一个旋转臂,它的方向即圆锥高的方向
- 已知长度和方向,我们可以得知这个 normal vector $\mathbf{n’} = \left | \frac{b}{\vert \mathbf{a} \vert } \right | \frac{\mathbf{a}}{\vert \mathbf{a} \vert} = \left | \frac{b}{\vert \mathbf{a} \vert^2 } \right | \mathbf{a}$
- (集合论)所有顶点到底面的连线的集合构成 hyperplane 的 vector space
Affine transformation $A(\mathbf{x}) = \mathbf{a} \cdot \mathbf{x} - b$ 的几何意义是:
- 以 $\mathbf{a}$ 为 x-axis,将空间内所有 $\mathbf{x}$ 压缩到一维,即压缩到 $\mathbf{a}$ 这个 x-axis 上
- $\mathbf{x}$ 压缩后位于 $x = \mathbf{a} \cdot \mathbf{x}$ 位置
- 将所有压缩后的 $\mathbf{x}$ 左移 $b$
- 此时位于 $x = 0$ 位置的所有 $\mathbf{x}$ 反压缩后即是 hyperplane vector space
- 此时原点位于 $x = -b$ 位置
- 这个长度为 $\vert b \vert$ 的移动距离反压缩后即是圆锥的高 $\left | \frac{b}{\vert \mathbf{a} \vert } \right |$
SVM
回头看这个 SVM 的最简单的 hard-margin 就很好懂了
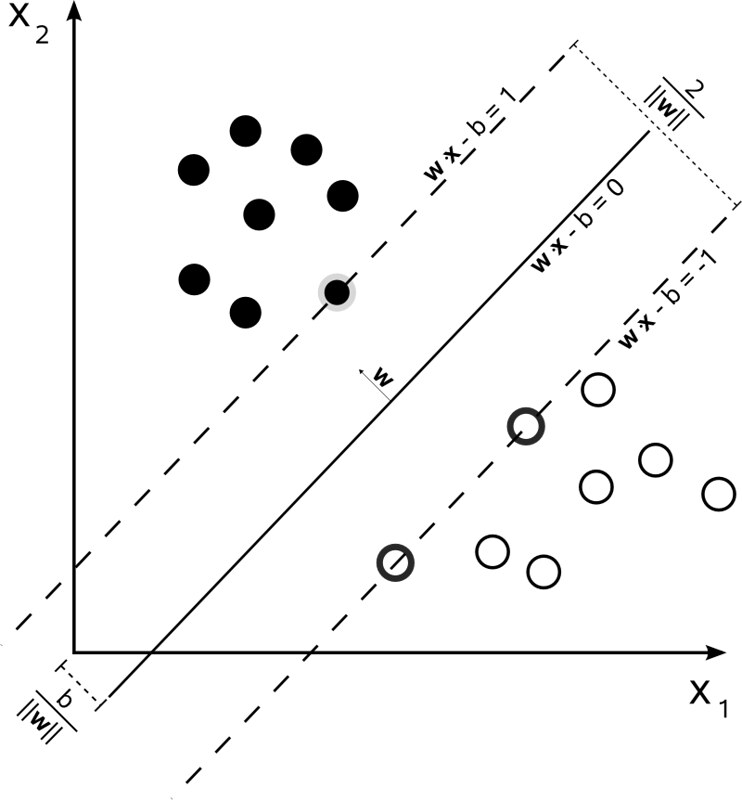
注意这个 margin 是设置成常数 1 还是符号 $c$ 并没有太大区别,因为最终都是可以通过 $\vert \mathbf{w} \vert$ 来调节的。
最终的 optimization problem:
“Minimize $|{\vec{w}}|$ subject to $y_{i}({\vec{w}} \cdot {\vec{x}}_{i}-b) \geq 1$, for $i=1,\,\ldots ,\,n$”.
这个图是 linear-separable (或者 precisely,hyperplane-separable) 的情况,如果是 non-linear-separable 的情况该怎么办呢?
用 kernel method
Kernel Method / Kernel Function
我们先看 Kernel Methods for Pattern Analysis 的定义:
Definition 2.8 [Kernel function] A kernel is a function $\kappa$ that for all $\mathbf{x}, \mathbf{z} \in X$ satisfies
\[\kappa(\mathbf{x}, \mathbf{z}) = \langle \phi(x), \phi(z) \rangle\]where $\phi$ is a mapping from $X$ to an (inner product) feature space $F$
\[\phi: \mathbf{x} \mapsto \phi(\mathbf{x}) \in F\]用到 SVM 里,基本思想就是:
- 你在 vector space $X$ 不是 hyperplane 不可分嘛,我把你 transform 到另外一个 vector space $F$,如果在 $F$ 里 hyperplane 可分,problem solved
- 我们需要用到 dot product,所以 $F$ 需要是个 inner product vector space
- 我们其实并不关心 transformation $\phi$ 是怎么个 transform 法,我们只关心 dot product $\phi(x) \cdot \phi(z)$
从定义可以看出:
- 这里 kernel 和 kernel function 是一个意思,而且和 Linear Algebra 里的 kernel 无关!(我宁愿你叫 inner-product method!)
- How to intuitively explain what a kernel is?: Kernel is a way of computing the dot product of two vectors in some (possibly very high dimensional) feature space, which is why kernel functions are sometimes called “generalized dot product”.
- 所以凡是涉及到 inner product 的 ML 算法,应该都可以用 kernel 处理
- 我能最快想到的场景就是 clustering,很多 metric 都可以用 inner product 表示
Normed Vector Space / Metric Space
Norms and Metrics, Normed Vector Spaces and Metric Spaces: Let $V$ be a vector space. A function $\vert \cdot \vert : V \to \mathrm{R}_{+}$ is a norm on $V$ if it satisfies:
- $\forall \mathbf{x} \in V: \vert \mathbf{x} \vert \geq 0$
- $\forall \mathbf{x} \in V: \vert \mathbf{x} \vert = 0 \Leftrightarrow \mathbf{x} = \mathbf{0} $
- $\forall \mathbf{x}, \mathbf{y} \in V: \vert \mathbf{x} + \mathbf{y} \vert \leq \vert \mathbf{x} \vert + \vert \mathbf{y} \vert$
- $\forall \alpha \in \mathrm{R}, \mathbf{x} \in V: \vert \alpha \mathbf{x} \vert = \alpha \vert \mathbf{x} \vert$
A vector space together with a norm is called a normed vector space.
Wikipedia: Metric space: A metric space is an ordered pair $(M,d)$ where $M$ is a set and $d$ is a metric on $M$, i.e., a function
\[d \colon M \times M \to \mathbb{R}\]such that for any $x,y,z \in M$, the following holds:
- (non-negativity or separation axiom): $d(x,y)\geq 0$
- (identity of indiscernibles): $d(x,y)=0 \Leftrightarrow x=y$
- (symmetry): $d(x,y)=d(y,x)$
- (subadditivity or triangle inequality): $d(x,z) \leq d(x,y)+d(y,z)$
Norms and Metrics, Normed Vector Spaces and Metric Spaces:
In other words, a normed vector space is automatically a metric space, by defining the metric in terms of the norm in the natural way. But a metric space may have no algebraic (vector) structure–i.e., it may not be a vector space–so the concept of a metric space is a generalization of the concept of a normed vector space.
所以,我们可以把 normed vector space 加上 inner product 操作,然后做成一个 inner product metric space。在这样一个 feature space 上的 clustering 应该都可以用 kernel method
更多 kernel clustering 内容参考 A Survey of Kernel Clustering Methods。
留下评论